|
| Adductor TendinopathyThis can be classified into 3 grades of pull or strain severity: 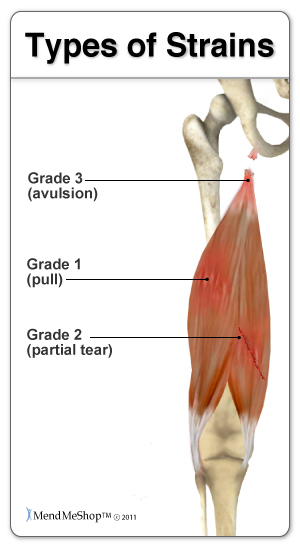 Minor - Grade 1 involve stretching of your muscles which results in slightly pulled muscles or very small tears in your muscles. You will generally feel mild cramping which will be a little tender or uncomfortable, but will involve no swelling or no loss of strength. Moderate - Grade 2 are more painful and involve a partial tearing of the tissue fibers in your muscle, tendon, or at the tendon attachment to your bone. You will generally experience some pain, along with swelling, decreased range of motion and strength, as well as difficulty walking or running. Your muscles will often be painful when you touch them. Severe - Grade 3 involve a complete tear (rupture) of your muscle fibers generally at your muscle/tendon and bone attachment; it is very painful and less frequent than the others. You will tend to experience a burning or stabbing pain, a lot of swelling and minimal strength, which may prevent you from walking without assistance or make it impossible for you to run. Bruising in the injured area is common a few days after the accident. This type of pull or strain may require a surgical repair. If you do not allow your tendons and muscles to heal properly, previous adductor injuries will build upon each other. The inability of your tendon to repair itself encourages micro-tears to accumulate faster than they can heal, increasing the breakdown of your tissue and reinforcing your pain and disability. The majority of adductor strains are grade 1 or 2 strains that involve partial tears, where your adductor tendon and muscle meet. (Also known as Adductor Tendinopathy, Adductor Tendonitis, Adductor Tendinosis, Groin Tendonitis, Groin Tendinopathy, Groin Tendinitis, Groin Tendinosis) Symptoms of Adductor Tendinitis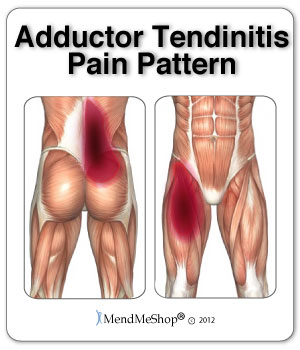 If you are suffering from Adductor Tendonitis you may have pain if you touch the area where tendon attaches in the pelvis. A sharp, stabbing pain may be experienced in your groin and inner thigh area. Pain levels raise when squeezing your legs together or when moving your affected leg away from the mid-line of the body. You may have ache or stiffness in the groin that increases with rest following or after a physically demanding activity. The pain in the groin and hip area develops gradually overtime. If you have a chronic injury, you may feel more of a dull ache that lasts for long periods of time. You may experience stiffness and decreased range of motion (ROM) in your hip joint as a result of injury in your short adductor muscles. This will make it more difficult to bend and rotate your hip and knee. If you have tightness, pain and/or tenderness while doing this, you are likely suffering from a damaged adductor. You may also feel tightness in your lower abdominal, spine and hip region. This is often more prevalent on the left than right side, however it is really dependent on your injury.  If the condition persists and becomes chronic Adductor tendonitis, you may experience pain symptoms that increase during activity. Your range of motion will be affected - so much so that you may limp as a result of the pain. Weakness of your adductor muscles can also be experienced as a result of adductor tendinitis or tendinopathy. This along with your other symptoms may make it difficult for you to walk or run and can result in you walking with a limp. Occasionally, bruising (broken blood vessels) in your groin area or over your adductor muscles may appear a few days after your injury. This may be in one spot or can span from your groin to your knees. Warmth, redness and/or a tender lump may accompany adductor tendinosis and severe cases of tendinitis. Swelling in your adductor muscles is a result of your tissues becoming inflamed; inflammation normally occurs with a more acute adductor strain and/or adductor tendinitis. Chronic cases will typically have little to inflammation. Causes of Adductor Tendinitis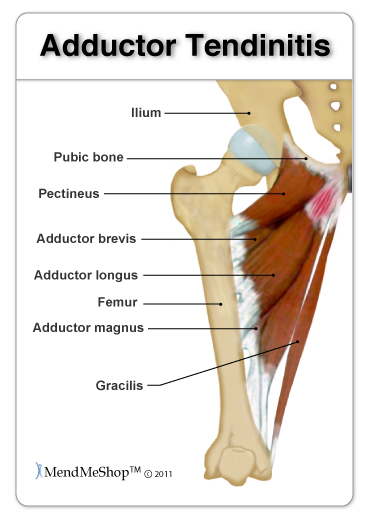 The most common cause of tendon inflammation is overuse of your area. It results from repetitive stress placed on your adductor muscles and tendons during active sports (especially when running, kicking, twisting, or side-stepping). Result of a sudden fall or direct hit, and/or overexerting yourself in everyday activities that involve twisting or lifting heavy objects while bending or running on an unstable surface (like grass or mud). Sports such as football, hockey and athletics (particularly sprinters, hurdlers, and long jumpers), skiing, horse riding and gymnastics, all commonly have Adductor tendonitis injuries. Alignment issues and leg length discrepancies, which affect the way you walk, or incorrect sport-specific motions, as well as strength differences in your muscles, lack of exercise and obesity, age-related weaknesses and/or degeneration, and genetics. Adductor Tendinitis: Reduce The Risk Avoid doing too much too soon - decrease, modify and/or avoid any activities that cause pain and irritation. Stabilize your groin, pelvis and hip area, build your core strength with light weights, exercise bands and balls, core balance training, and exercises to develop strength, speed and agility, such as jumping or bounding. Yoga, Tao chi, or a daily stretching routine will also help keep your muscles and joints supple, and will increase your range of motion. Combine these with regular low-impact exercise and healthy diet. Always warm up and cool down your muscles, learn the proper form and techniques to prevent injuries, and utilize any available mobility supports (braces, taping, orthotics, canes) to help alleviate undue stress and improve your function. Adductor Tendinitis DiagnosisGroin pain is often difficult to diagnose, especially when chronic; however, adductor tendinitis is among the most frequent and easily identified groin related pain. To help your doctor achieve a proper diagnosis, he/she will begin with a medical history about you, your current condition and symptoms. He/she will inquire about the intensity of your present pain, the duration of your symptoms and the limitations you are experiencing. Details about the injury, when it started, and whether or not you have ever had treatments for this or a similar condition in the past, will be very helpful in assessing your injury.  A physical examination will be performed to determine if you have any signs of adductor tendinitis or tendinopathy. Your doctor will look and feel the muscles, bones and other soft tissue in and around your pelvis and groin area (near and/or including your genital area) as well as your hip, spine, and lower body to evaluate sameness, recognize differences and identify pain and tenderness. This will help to discover any abnormalities, such as mild or severe inflammation, fluid, bruising, bone or tissue deformity. He/she may ask you to complete a series of hip and leg movements to see what motions cause pain, weakness or instability, such as contracting your adductor muscles against resistance. This will help to determine the location of your injury and test for the grade of your adductor injury. He/she will also check the way you walk (gait) to determine if you have any adductor or other muscle weakness. Common Adductor Tendinopathy Diagnostic Tests:X-rays will provide a two-dimensional image of the overall structure of your pelvis and groin. They are helpful in identifying pelvis instability, fractures, abnormal bone shapes (bone spurs or bone cysts, wear and tear on the joints) and/or other groin or hip problems. Isotope Bone Scans are used to identify bone abnormalities, such as a tear, inflammation, fracture or infection of the pubic bone. It will also identify whether other groin conditions are present (osteitis pubis, sports hernia, fractures). 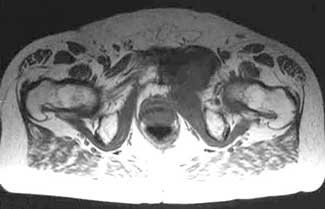 MRIs (magnetic resonance imaging) will provide more detailed information and will help to evaluate the soft tissues in and around your groin and pelvis (muscles, tendons, ligaments, fascia, and other connective tissues). It can identify ligament or tendon damage, and can help to determine the extent of your injury, the grade of your tear or inflammation, as well as other associated groin conditions. Diagnostic ultrasound (Ultrasonography) or CT scans (computerized tomography) can be used to provide a more thorough 2 or 3-dimensional assessment of the soft tissues, organs and bones in and around your groin and pelvis. Ultrasound is useful for diagnosing and locating muscle and tendon tears, but not tendinopathy. Treating Adductor TendinitisInitial treatment should focus on resting your leg/hip/groin and reducing the inflammation to help relieve pain. Do not train through the pain. It may be necessary to stop work and activity for a few weeks or more. The good news is that most cases of Adductor Tendinitis will heal with simple home conservative treatments and surgery is often not needed! First you need to stop the activity that is causing your pain and rest your hip and groin. Adductor Tendon Home Conservative Treatment OptionsStep 1 - Reduce Pain and Swelling with Cold CompressionThe first step for conservative treatment of your hip tendinitis is to reduce the swelling to "open up" the area for more blood flow. Anyone in the health-care business knows that your blood supplies the oxygen and much needed nutrients required to heal hip tendinitis injuries. This is why for years, doctors, trainers, and other medical professionals have recommended RICE (Rest, Ice, Compression, Elevation) to treat the pain and swelling of fresh injuries, chronic pain, and after any re-injury. Cold Compression Slows nerve and tissue function - reducing the swelling that blocks blood vessels from doing their job. This is important because once blood vessels are blocked or damaged, they can no longer carry oxygenated blood through the tissue and tissues begin to break-down. Without cold compression, tissue break-down continues as they don't get the oxygen they need to survive. By limiting the amount of damage done to your tendon, you also limit the amount of healing that needs to occur. This is a very important step to heal tendon injuries faster and with less pain! This is why you need to treat your hip pain right after it's hurt, when you notice pain / swelling / inflammation, or directly after a re-injury. Applying a Cold Compress or Ice Pack right away will help stop the damage immediately and unblock your blood vessels to let your body's natural blood flow in to start healing the tissue. Use a Cold Compress or Ice Pack:
Step 2 - Improve Circulation, Soften Scar Tissue & Prevent Re-Injury with a Leg TShellz Wrap®After the inflammation in your groin has been reduced, providing extra blood flow and strengthening soft tissue in the injured area is recommended. TShellz Wraps® contain a unique Carbon Fiber Energy Pad which is flexible and will shape to conform to your body. This Energy Pad emits a uniform wave of perfectly safe energy over its entire surface. This energy is absorbed by soft tissue in the treatment area, opening blood vessels, resulting in an increase in blood flow. Increased blood circulation is what your body needs to accelerate the healing of soft tissue and this is why we recommend the TShellz Wrap®. 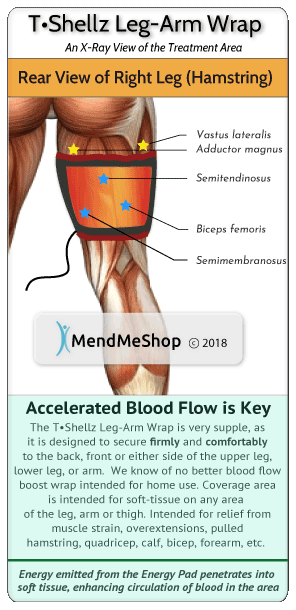
Use Circulatory Boost TShellz Wraps®:
The TShellz Wrap® is an FDA Registered Medical Device and is suitable for use in therapeutic clinics and FROM HOME. It is completely safe for people and patients to use for themselves. The technology found in a TShellz Wrap® has been used for decades in the worlds of professional and amateur sports - a contributing factor as to why athletes seem to recover from injuries so quickly. Have you ever wondered by an athlete can return to activity after 3 or 4 weeks following a tendon injury - while your average person takes much longer to return back to normal? The secret isn't really that much of a secret - it involves consistent treatments (meaning multiple times a day) using a treatment like the TShellz Wrap® to stimulate blood flow to the injured tissues. Most athletes have the luxury of using in-house facilities many times per day. How many us can afford the time and money to visit a clinic multiple times a day? Very few indeed. This is how you can gain some of the advantages that athletes enjoy in their injury recovery - by using a device like the TShellz Wrap® two or three times a day on a consistent basis. Consistent Treatments = Consistent And Long Term ImprovementConservative Treatment Tools Our Clients Have Used to Help |
        |


















