|
|
Is It Really Tendonitis?Cyst vs Tendonitis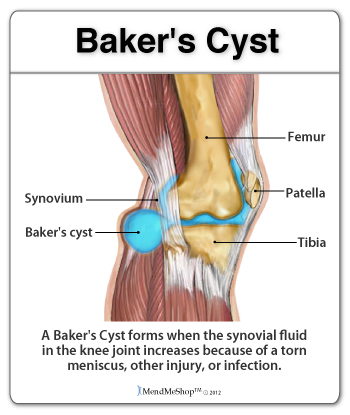 A ganglion cyst or synovial cyst can occur in any joint in the body. They appear under the skin as a lump or bump (non-cancerous) and may sometimes present no other symptoms. The cyst is basically a soft sac filled with a thick, clear fluid. It's still unknown why cysts form so close to a joint or tendon. They may or may not become painful (in a lot of cases they're harmless), will limit your activity and could possibly grow larger if you continue the activity that caused this injury in the first place. Usually cysts only become really painful if the cyst is pressing down on any nerves in the affected area. If this is the case, then you may suffer from pain, tingling, numbness or muscle weakness. If you don't have a lot of pain then you may only need to treat the symptoms of your cyst and wait for the cyst to naturally go away on its' own. Cysts most commonly show up in the wrist, hand, ankle, feet and near other joints (ie. the back of the knee - a baker's cyst). Bursitis vs Tendonitis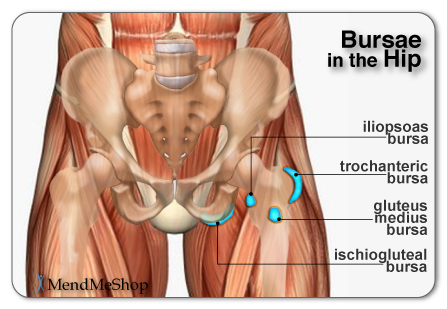 Bursae (plural for bursa) are flattened fluid-filled sacs that function as cushions between your bones and muscles (deep bursae) or bones and tendons (superficial bursae). They reduce friction and allow the surface of your soft tissue to slide over bone effortlessly. When pressure or friction is too great, excess fluid can build up in the bursa sac causing inflammation. When a bursa becomes inflamed, moving the affected area becomes very painful and movement can be difficult. Any actions that put pressure on the inflamed bursa can increase irritation and cause further inflammation and pain. Calcific Tendinitis vs Tendonitis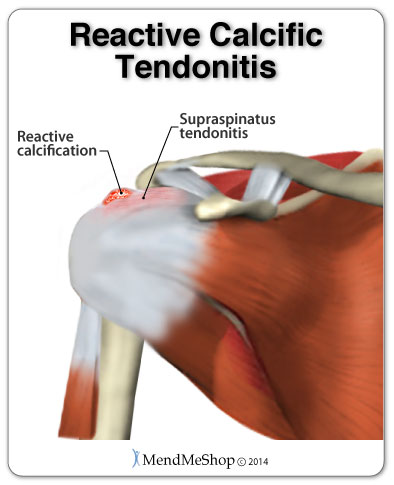 Calcific Tendonitis is caused by a chemical reaction with other tissues in the body - resulting in calcium that builds-up in the tendons. This is a more common condition with women between the ages of 30 and 50. This is not a sport / activity related injury. Calcific Tendonitis is known to be a natural process than can occur in some people and not in others. The shoulder and rotator cuff are the typical location of calcific tendinitis, but it can also occur in the elbows, wrists, hands, hips, knees, or feet. In some cases this injury can also be called calcific tendinopathy. With this condition you may experience pain and stiffness that often comes back. Calcific tendonitis usually only lasts for one to two months. Arthritis vs Tendonitis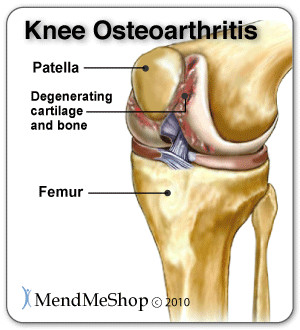 Arthritis is a condition that can affect the tissue lining in joints (this lining is called the 'synovium'). You may suffer from rheumatoid arthritis (RA) which is an autoimmune disease, or osteoarthritis (OA) which is a degenerative condition from wear and tear. When experiencing arthritis in general, inflammation from arthritis causes redness, heat, pain and swelling. Symptoms start with feeling pain and stiffness in the joint, reduced joint mobility, and swelling. It's possible for arthritis to cause tendonitis, with severe swelling in the joint arthritis can cause weakening in tendon tissue resulting in a strain or rupture. Autoimmune Diseases vs TendonitisAutoimmune diseases can affect almost any part of the body, including the heart, brain, nerves, muscles, skin, eyes, joints, lungs, kidneys, glands, the digestive tract, and blood vessels. The classic sign of an autoimmune disease is inflammation, which can cause redness, heat, pain, and swelling. If the disease affects the joints, as with arthritis or systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), you might have joint pain, stiffness, and loss of function. How Can I Prevent Tendonitis?
Product Advisors are available 9:00 am to 5:00 pm Eastern Standard Time Monday to Friday. Learn More About Tendon Injuries & TreatmentsI want to learn more about Post-Surgery Recovery I want to learn more about TShellz Wrap® Circulatory Boost I want to learn more about Ice & Heat: Which Is Better For Treatment? I want to learn more about Tendonitis Treatments I want to learn more about Tendonitis Surgery FREE SHIPPING ON ALL PRODUCTS CURRENTLY ENABLED |
           |

